Title: Cubist Bird
Creator: Sargent Claude Johnson
Creator Lifespan: 1888/1967
Creator Gender: Male
Creator Birth Place: Boston, Massachusetts
Date Created: 1967
Physical Dimensions: w393.7 x h304.8 in
Type: Enamel on steel
logistic回归不是回归,而是分类
sigmoid函数
在直接写logistic regression的相关公式之前,先来介绍下sigmoid函数
Sigmoid function,一般简称S函数,其形状如下:
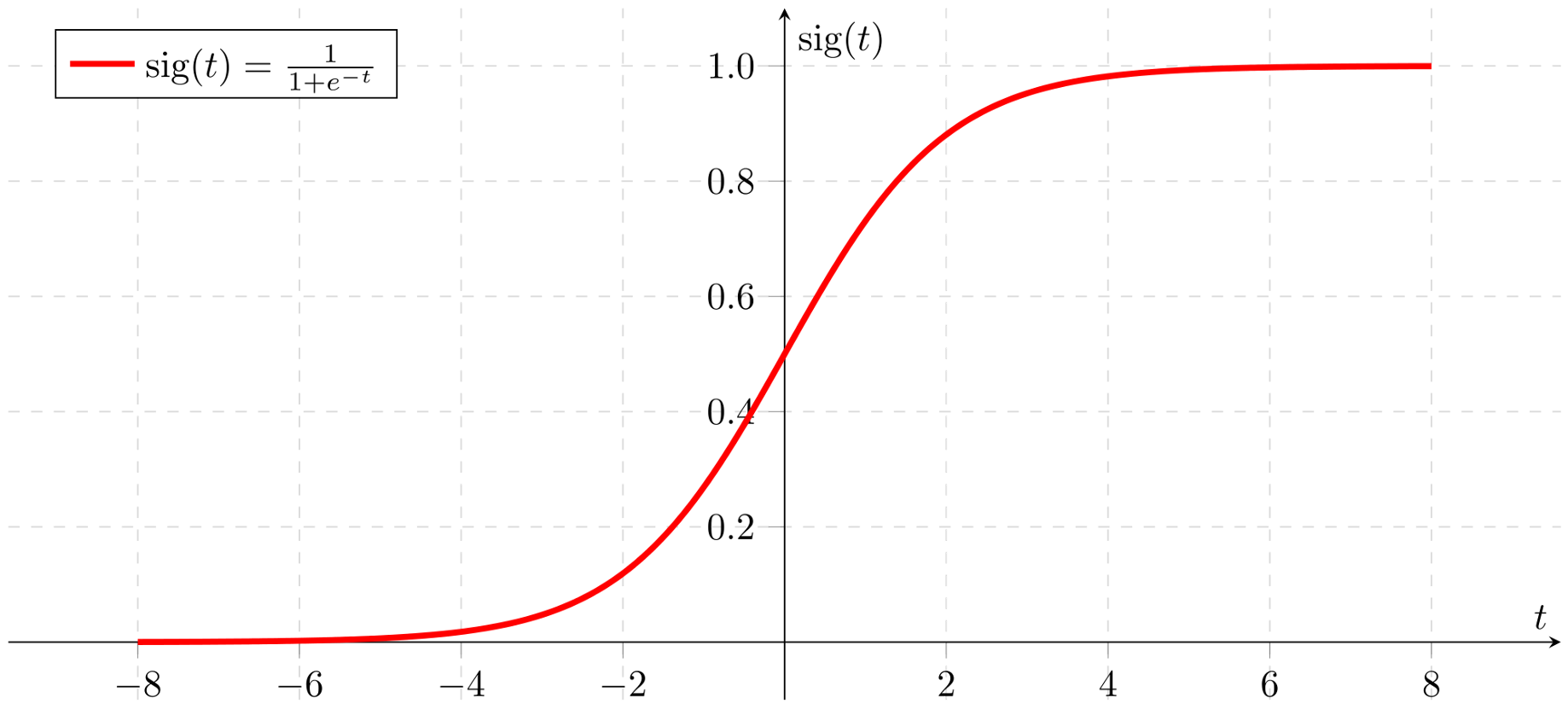
其表达式为: $ g(z) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-z}} $
- sigmoid函数的值在0~1之间
- sigmoid函数求导后的值为:$g’(x) = g(x)·(1-g(x))$
Hypothesis
假设: $ h_\omega(x) = g(\omega^T x) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-\omega^Tx}} $
从公式推导来说,这里应该是”$\omega x+b$”,只是在coding时一般把b加到了”$\omega;x=1$”中,不再单独列出来。影响不大。
$h_\omega(x)$表示在$\omega$确定的情况下,根据$x$计算出的结果输出为1的可能性,即后验概率: \(h_\omega(x) = P(y=1|x;\omega)\)
用概率表来描述分类器,比阶跃形式更加顺滑,更加连续。
Cost
- loss,这里采用对数损失函数
- 不用linear regression一样选用平方损失函数是因为:将上述$h_\omega(x)$带入平方loss后得到的是非凸函数,后续梯度下降法不一定能得到全局最优解,很可能得到的是局部最优。选用对数loss能得到凸函数。
公式: $ L(f)=L(h_\omega(x)) = -y·logP(y|x) = -y·log(h_\omega(x)) - (1-y)·log(1-h_\omega(x)) $
Optimization
问题即求cost最小时的$\omega$的取值
采用Gradient Descent方法来求解$minimize(loss)$
令:
$W = (\omega_1, \omega_2, \omega_3, …, \omega_n, b)^T $
$X = (x_1, x_2, x_3, …, x_n, 1)^T $
$Y = (y_1, y_2, y_3, …, y_n)^T $
则:
$
J(\omega) = minimize(loss) = arg min(-y·log(h_\omega(x)) - (1-y)·log(1-h_\omega(x)))
$
为求极小值,对其进行求导:
$
\frac{\partial J(\omega)}{\partial \omega} = (h_\omega(x)-y)x
$
很巧合的是,这里求导得到的结果的形式与linear regression求导得到的形式一致,但是实质上将$h_\omega(x)$带入后结果是不一样的
梯度方向即为导数方向,沿着梯度下降则为:
$
\omega_j = \omega_j - \alpha \frac{\partial J(\omega)}{\partial \omega_j}
$
更新$\omega$的值,即为训练阶段
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
# coding=UTF-8
'''
@Author: Yewbs Wei
@Date: 2019-08-05 17:58:35
@LastEditors: Yewbs Wei
@LastEditTime: 2019-08-06 17:30:33
@Description: 使用梯度下降方法实现Logistic Regression
'''
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
class LogisticRegression():
def __init__(self, X_train, Y_train, learning_rate=0.1, epochs=10000, threshold=0.0001):
self.X_train = X_train
self.Y_train = Y_train
self.theta = np.random.rand(1, self.X_train.shape[1] + 1)
self.grad = None
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.epochs = epochs
self.threshold = threshold
self.cost = None
def sigmoid(self, x):
'''
@description: 计算sigmoid函数: 1/(1+e^(-x))
@param {type}
@return:
'''
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
def logistic_hypo(self, x):
'''
@description: 计算hypothesis
x = (x1, x2, x3, ..., xn, 1)
@param {type}
@return:
'''
return self.sigmoid(np.dot(np.c_[np.ones(x.shape[0]), x], self.theta.T))
def logistic_cost(self, x, y):
'''
@description: 计算损失
@param {type}
@return:
'''
y_hat = self.logistic_hypo(x)
self.cost = - np.sum((y * np.log(y_hat) + (1.0 - y) * np.log(1.0 - y_hat)))
self.cost = self.cost * 1.0 / x.shape[0]
def logistic_grad(self, x, y):
'''
@description: 计算梯度
@param {type}
@return:
'''
self.grad = np.dot((self.logistic_hypo(x) - y).T, np.c_[np.ones(x.shape[0]), x])
self.grad = self.grad / x.shape[0]
def logistic_grad_desc(self):
'''
@description: 用梯度下降法来进行优化
@param {type}
@return:
'''
self.logistic_cost(self.X_train, self.Y_train)
cost_change = 1.0
i = 1
while cost_change > self.threshold and i < self.epochs:
# 沿着梯度的方向更新参数theta的值
self.logistic_grad(self.X_train, self.Y_train)
self.theta = self.theta - self.learning_rate * self.grad
pre_cost = self.cost
self.logistic_cost(self.X_train, self.Y_train)
cost_change = abs(self.cost - pre_cost)
i += 1
if i%100 == 0:
# 每100次输出一次loss大小
print("-------%d ---- loss = %f" %(i ,self.cost))
def fit(self):
'''
@description: emm, sklearn里面的fit函数
@param {type}
@return:
'''
self.logistic_grad_desc()
# def predict(self, x):
# '''
# @description: 预测
# @param {type}
# @return:
# '''
# y_pre = self.logistic_hypo(x)
# return y_pre
def predict(self, X, hard=True):
'''
@description: 预测
@param {type}
@return:
'''
X = (X - np.mean(X, axis=0)) / np.std(X, axis=0)
pred_prob = self.logistic_hypo(X)
pred_value = np.where(pred_prob > 0.5, 1, 0)
if hard:
return pred_value
else:
return pred_prob
def main():
# test
# 加载sklean中自带的数据集
dataset = datasets.load_iris()
# 选择维度
X = dataset.data[0:100, 0:2]
Y = dataset.target[:100, None]
# 切分数据集为训练集和测试集
idx_trn = list(range(30))
idx_trn.extend(range(50, 80))
idx_tst = list(range(30, 50))
idx_tst.extend(range(80, 100))
X_train = X[idx_trn]
X_test = X[idx_tst]
Y_train = Y[idx_trn]
Y_test = Y[idx_tst]
lr = LogisticRegression(X_train, Y_train)
lr.fit()
y_pre = lr.predict(X_test)
print(y_pre - Y_test)
main()